Hold-Tap Behavior
Summary#
Hold-tap is the basis for other behaviors such as layer-tap and mod-tap.
Simply put, the hold-tap key will output the 'hold' behavior if it's held for a while, and output the 'tap' behavior when it's tapped quickly.
Hold-Tap#
The graph below shows how the hold-tap decides between a 'tap' and a 'hold'.
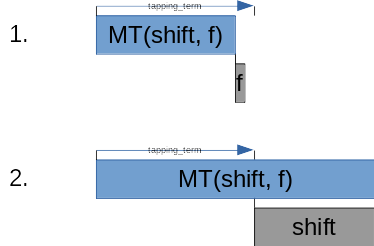
By default, the hold-tap is configured to also select the 'hold' functionality if another key is tapped while it's active:

We call this the 'hold-preferred' flavor of hold-taps. While this flavor may work very well for a ctrl/escape key, it's not very well suited for home-row mods or layer-taps. That's why there are two more flavors to choose from: 'tap-preferred' and 'balanced'.
Flavors#
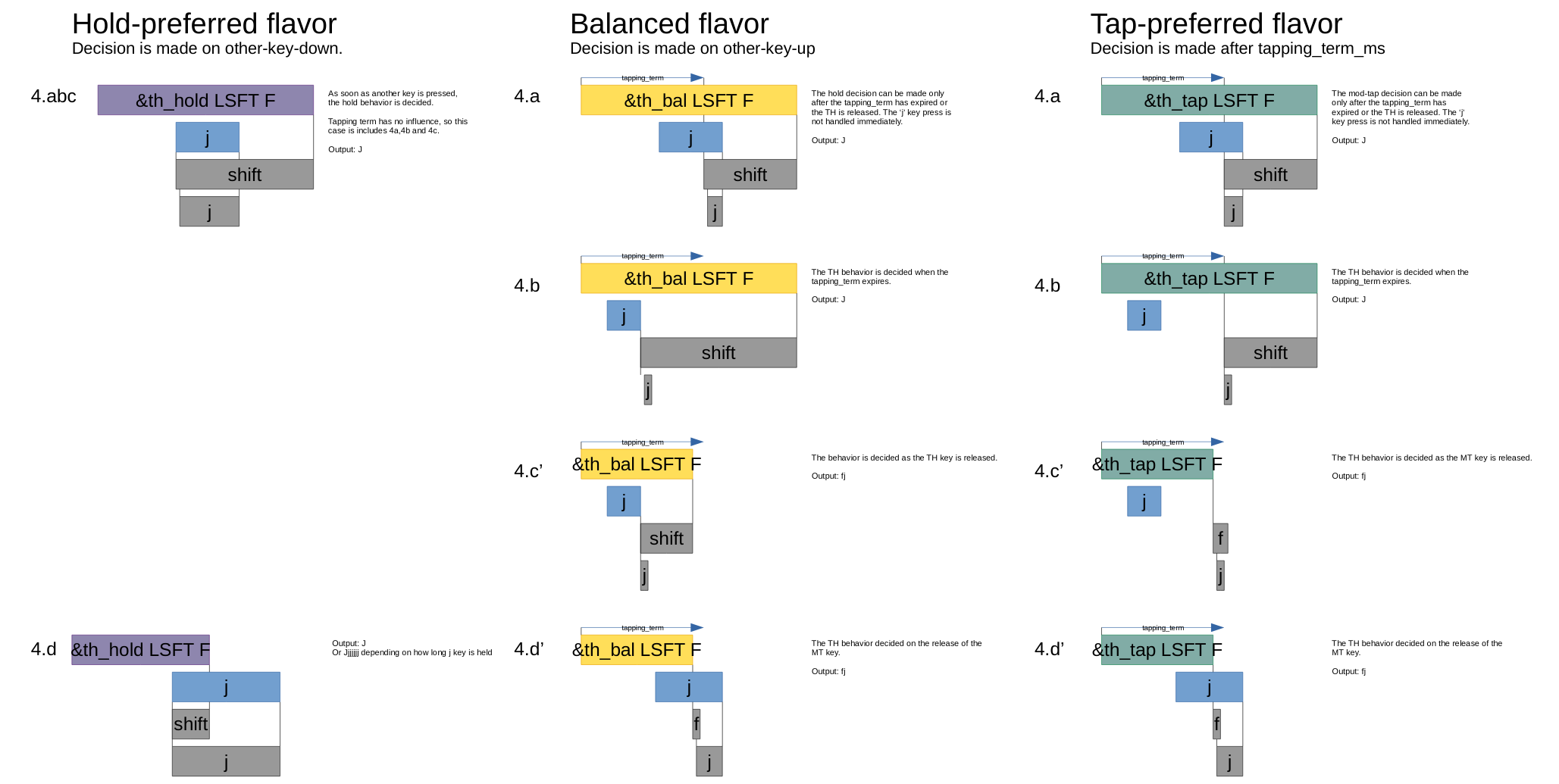
- The 'hold-preferred' flavor triggers the hold behavior when the
tapping-term-mshas expired or another key is pressed. - The 'balanced' flavor will trigger the hold behavior when the
tapping-term-mshas expired or another key is pressed and released. - The 'tap-preferred' flavor triggers the hold behavior when the
tapping-term-mshas expired. It triggers the tap behavior when another key is pressed. - The 'tap-unless-interrupted' flavor triggers a hold behavior only when another key is pressed before
tapping-term-mshas expired. It triggers the tap behavior in all other situations.
When the hold-tap key is released and the hold behavior has not been triggered, the tap behavior will trigger.
Basic usage#
For basic usage, please see mod-tap and layer-tap pages.
Advanced Configuration#
tapping-term-ms#
Defines how long a key must be pressed to trigger Hold behavior.
quick-tap-ms#
If you press a tapped hold-tap again within quick-tap-ms milliseconds, it will always trigger the tap behavior. This is useful for things like a backspace, where a quick tap+hold holds backspace pressed. Set this to a negative value to disable. The default is -1 (disabled).
In QMK, unlike ZMK, this functionality is enabled by default, and you turn it off using TAPPING_FORCE_HOLD.
retro-tap#
If retro tap is enabled, the tap behavior is triggered when releasing the hold-tap key if no other key was pressed in the meantime.
For example, if you press &mt LEFT_SHIFT A and then release it without pressing another key, it will output a.
&mt { retro-tap;};Positional hold-tap and hold-trigger-key-positions#
- Including
hold-trigger-key-positionsin your hold-tap definition turns on the positional hold-tap feature. - With positional hold-tap enabled, if you press any key NOT listed in
hold-trigger-key-positionsbeforetapping-term-msexpires, it will produce a tap. - In all other situations, positional hold-tap will not modify the behavior of your hold-tap.
- Positional hold-tap is useful with home-row modifiers. If you have a home-row modifier key in the left hand for example, by including only keys positions from the right hand in
hold-trigger-key-positions, you will only get hold behaviors during cross-hand key combinations. - Note that
hold-trigger-key-positionsis an array of key position indexes. Key positions are numbered according to your keymap, starting with 0. So if the first key in your keymap is Q, this key is in position 0. The next key (probably W) will be in position 1, et cetera. - See the following example, which uses a hold-tap behavior definition, configured with the
hold-preferredflavor, and with positional hold-tap enabled:
#include <dt-bindings/zmk/keys.h>#include <behaviors.dtsi>/ { behaviors { pht: positional_hold_tap { compatible = "zmk,behavior-hold-tap"; label = "POSITIONAL_HOLD_TAP"; #binding-cells = <2>; flavor = "hold-preferred"; tapping-term-ms = <400>; quick-tap-ms = <200>; bindings = <&kp>, <&kp>; hold-trigger-key-positions = <1>; // <---[[the W key]] }; }; keymap { compatible = "zmk,keymap"; label ="Default keymap"; default_layer { bindings = < // position 0 position 1 position 2 &pht LEFT_SHIFT Q &kp W &kp E >; }; };};- The sequence
(pht_down, E_down, E_up, pht_up)producesqe. The normal hold behavior (LEFT_SHIFT) IS modified into a tap behavior (Q) by positional hold-tap because the first key pressed after the hold-tap key is theE key, which is in position 2, which is NOT included inhold-trigger-key-positions. - The sequence
(pht_down, W_down, W_up, pht_up)producesW. The normal hold behavior (LEFT_SHIFT) is NOT modified into a tap behavior (Q) by positional hold-tap because the first key pressed after the hold-tap key is theW key, which is in position 1, which IS included inhold-trigger-key-positions. - If the
LEFT_SHIFT / Q keyis held by itself for longer thantapping-term-ms, a hold behavior is produced. This is because positional hold-tap only modifies the behavior of a hold-tap if another key is pressed before thetapping-term-msperiod expires.
Home row mods#
The following are suggested hold-tap configurations that work well with home row mods:
Option 1: cross-hand only modifiers, using tap-unless-interrupted and positional hold-tap (hold-trigger-key-positions)#
#include <dt-bindings/zmk/keys.h>#include <behaviors.dtsi>/ { behaviors { lh_pht: left_hand_positional_hold_tap { compatible = "zmk,behavior-hold-tap"; label = "LEFT_POSITIONAL_HOLD_TAP"; #binding-cells = <2>; flavor = "tap-unless-interrupted"; tapping-term-ms = <100>; // <---[[produces tap if held longer than tapping-term-ms]] quick-tap-ms = <200>; bindings = <&kp>, <&kp>; hold-trigger-key-positions = <5 6 7 8 9 10>; // <---[[right-hand keys]] }; };
keymap { compatible = "zmk,keymap"; default_layer { bindings = < // position 0 pos 1 pos 2 pos 3 pos 4 pos 5 pos 6 pos 7 pos 8 pos 9 pos 10 &lh_pht LSFT A &lh_pht LGUI S &lh_pht LALT D &lh_pht LCTL F &kp G &kp H &kp I &kp J &kp K &kp L &kp SEMI >; }; };};Option 2: tap-preferred#
#include <behaviors.dtsi>#include <dt-bindings/zmk/keys.h>
/ { behaviors { hm: homerow_mods { compatible = "zmk,behavior-hold-tap"; label = "HOMEROW_MODS"; #binding-cells = <2>; tapping-term-ms = <150>; quick-tap-ms = <0>; flavor = "tap-preferred"; bindings = <&kp>, <&kp>; }; };
keymap { compatible = "zmk,keymap"; default_layer { bindings = < &hm LCTRL A &hm LGUI S &hm LALT D &hm LSHIFT F >; }; };};
Option 3: balanced#
#include <behaviors.dtsi>#include <dt-bindings/zmk/keys.h>
/ { behaviors { bhm: balanced_homerow_mods { compatible = "zmk,behavior-hold-tap"; label = "HOMEROW_MODS"; #binding-cells = <2>; tapping-term-ms = <200>; // <---[[moderate duration]] quick-tap-ms = <0>; flavor = "balanced"; bindings = <&kp>, <&kp>; }; };
keymap { compatible = "zmk,keymap"; default_layer { bindings = < &bhm LCTRL A &bhm LGUI S &bhm LALT D &bhm LSHIFT F >; }; };};
Comparison to QMK#
The hold-preferred flavor works similar to the HOLD_ON_OTHER_KEY_PRESS setting in QMK. The 'balanced' flavor is similar to the PERMISSIVE_HOLD setting, and the tap-preferred flavor is similar to IGNORE_MOD_TAP_INTERRUPT.